Definition of Breech presentation
Breech presentation is when the buttock of the fetus enters to pelvis before heading of the baby. It comprises of 3 – 4% of singleton delivery at term.
What are the risk factors?
Risk factors can be fetal or maternal.
Fetal risk factors
- Macrosomia
- Multifetal gestation
- Polyhydramnios
- Hydrops fetalis
- Congenital muscular dystrophies
- Extended leg
- Fetal anomaly like hydrocephalus
Maternal risk factors
- Family and history of breech
- Contracted pelvis
- Uterine congenital anomaly
- Uterine myoma
- Grand multiparity
- Preterm labor and delivery
Types of Breech presentation
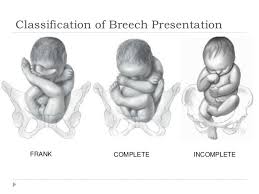
Frank Breech
The fetus flexes his leg at the hip joint but extends at the knee joint and it comprises 65% of breech presentation. The risk of cord prolapse is only 1% which is similar to vertex presentation.
Complete Breech
The fetus flexes his leg both at the hip and knee joint. It comprises 10% of breech presentation. And the risk of cord prolapse is 5% here.
Footling breech
It is also called incomplete breech. This is the second commonest type of breech presentation. It comprises 25% of the cases. This is the type where the baby enters the canal with his or her foot. It can be felt by the examiner’s finger during a vaginal exam.
The risk of cord prolapse is 15% here so the delivery should be with C – section.
How to diagnosis breech presentation?
What do we find in History & Physical examination?
History
The mother mostly complains of epigastric pain because the hard part of the fetus (head of the fetus) presses against the diaphragm and stomach in breech presentation.
Physical examination
On Leopold examination – Hard, round, and ballotable mass are what occupied the fundus. And fHB better auscultated above the umbilicus, unlike cephalic presentation.
PV examination – Depend on the type, PV findings are also different. For example, in the footling breech, we palpate the foot of the baby during PV examination. We can palpate the ischial tuberosity and anus of the fetus. But it might be difficult to differentiate complete breech and face presentation.
How to differentiate the face presentation from the breech presentation on PV examination?
- Muscular resistance increase in the anus so if you feel muscular resistance during PV examination, that is breech presentation.
- Presence of meconium indicates breech presentation.
- Mouth and molar eminence form a triangle shape in face presentation but ischial tuberosity and anus lie in a straight line in breech presentation.
Ultrasound
U/S is a very useful diagnostic tool to confirm the presentation. It also needs to estimate fetal size, assesses the attitude of the fetal head to rule out hyperextension of the head (stargazer fetus or flying fetus).
It also helps to rule out congenital anomaly (the rate of congenital anomaly is 6.3% in the breech presentation which is a high proportion compared to the cephalic presentation which is 2.4%).
Complications of Breech Presentation
Breech presentation is one of abnormal presentation. And it has many complications both for the mother and the fetus.
Maternal complications
- It increases the operative delivery rate
- Increased genital tract laceration
- Increase the risk of infection due to manual manipulation during delivery
Fetal complications
Breech presentaiton has increase risk of
- Cord prolapse
- Birth trauma
- Birth asphexia
- Preterm labor
- Congential anomaly
- Birth trauma
Mechanism of Labor in Breech Presentation
The mechanism of labor in breech is different than in the cephalic. Here is mechanism of labor in breech.
- Engage – trochanteric diameter enter the pelvis in a transverse position.
- Decent
- Internal rotation
- Lateral flexion, and
- Delivery of breech – shoulder enter to pelvis with bisacromial diameter transverse and rotate 90 degrees and emerge oblique or AP diameter. The Head rotates 90 degrees and delivers it after the neck is seen.
Read about mechanism of labor in cephaic presentation.
Management of Breech Delivery
There are 3 options of delivery. These are: –
- Version
- C-section
- Vaginal breech delivery
Version
This is changing the presentation of the fetus by turning it upside down. It can be an internal podalic version or an external cephalic version.
Internal Podalic Version
This is done by a specialized doctor after the amniotic membrane is ruptured. The doctor turns the baby upside down internally. It is mostly used to deliver the 2nd breech twin after the first one is already born. The steps are explained on the video.
External Cephalic Version
This method is used to turn the fetus from breech or transverse to vertex position before labor begins (after 36 weeks). And its success rate is around 58% on average.
Newman develops the score to predict the success rate of the external cephalic version. See the video to understand the steps.
C-Section Delivery
There are different indication to do C-Section in breech. These are: –
- Footling breech
- In twin pregnancy – if the first twin is breech.
- Other C-section indications