The menstrual cycle is a natural phenomenon that results in monthly uterine bleeding in women. And understanding a scientific explanation behind it helps you to know if yours is normal or not.
Menus usually start around 10 -16 age ( menarche ) and stop at 45 -55 years of age which is called menopause. The cycle can be normal or abnormal. We will see more about that later.
Scientific background on how the menstrual cycle occurs? What are the hormones involved?
Nature finds a way to design a perfect cycle due to hormonal effects. And ovaries and endometrium are involved in the process.

Endometrial phase – Proliferative, Secretory & Menstrual bleeding
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. And it has 2 zones. Functional layer and basalis layer.
The functional layer is the superficial layer which shades during menus. It consists of epithelium, gland, stroma, and capillary plexus. And basalis layer is the lower layer which is less hormonal sensitive. So its use is mainly for regeneration.
The 3 endometrial phases during the menstrual cycle. And these are: –
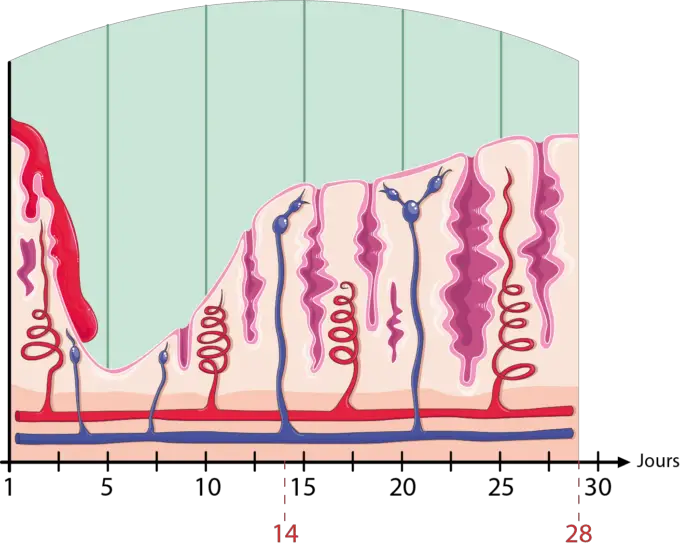
- Proliferative phase (occur from day 5 – 14)
At this phase of menus, the endometrium is thick and has more vascularity. The gland becomes is straight. - Secretory phase (occur from day 15 – 28)
At this point, endometrial glands become more tortuous and dilated. Spiral arteries become enlarged and coiled. - Menus (occur from day 1 – 5)
This is the time a woman sees bleeding which is called menus. At this point, vessels rupture, and endometrium start to regenerate.
Ovarian cycle – Follicular development, Ovulation & Luteal phase
Every month 25 – 30 follicle began to develop within the ovary. But only 1 ovary will fully be developed and released.
Ovaries go through 3 phases during the menstrual cycle.
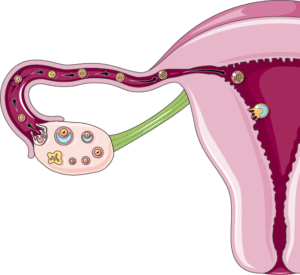
- Follicular phase (occur from day 1 – 14)
- Ovulation – (day 14)
- Luteal phase – (day 14 – 28)
The follicular phase is further divided into 2. Early and late. In the early follicular phase, FSH will be stimulated and ovarian follicles began to grow. In the late follicular phase, one follicle becomes dominant and estrogen production will be increased which results in an LH surge. LH will trigger ovulation which occurs on day 14 of the menstrual cycle. After ovaries release the dominant follicle, the remaining become corpus luteum. it produces progesterone for up to 14 days. Then both progesterone and estrogen level will fall which result in uterine bleeding (menses).
How do I know if I have a normal or abnormal menstrual cycle?

What is the normal menstrual cycle?
Normal menstrual cycle means normal duration, cycle, and amount of menus with mild pain. So the range should be between the following numbers.
- Cycle is every – 21 – 35 days (28 days + or – 7)
- Menstrual duration – 2 – 8 days
- Amount – 20 – 80 ml
- Pain – mittelschmert , dull aching or pressure which start 2 – 3 days before menses.
Anything out of this range is considered abnormal and if you have an abnormal census, you should go to the doctor and check if everything is okay.
What is abnormal menstruation?
It is either an abnormal cycle or an abnormal duration.
Abnormal cycle includes
- Oligomenorrhea – menses at an interval of more than 35 days.
- Amenorrhea – the absence of menses
- Polymenorrhea – menses at an interval of fewer than 21 days.
Abnormal duration includes
- Menorrhagia (hypermenorrhea) – Heavy menstrual bleeding either more than 80 ml of blood or stay more than 7 days is called menorrhagia. The problem here is the amount and menstrual length.
- Metrorrhagia and
- Hypomenorrhea – light period flow. Here the duration and frequency are normal. The problem is the amount of bleeding.
What to do if you have abnormal uterine bleeding
There are many causes which result in abnormal uterine bleeding (abnormal menstrual cycle). To mention some of them,
- Polyp
- Adenomyosis
- Myoma
- Malignancy like uterine and cervical cancer
- A bleeding disorder (coagulopathy)
- Ovulatory dysfunction
- Endometrial causes
- It can also be iatrogenic causes. So if you experience abnormal uterine bleeding, you should go to the doctor.

Pingback: Iron Deficiency Anemia - Risk Factors, Symptoms and Treatment
Pingback: Von Willebrand disease (Types and Treatment) - Life As MD